NIRSpec Optics
NIRSpec is an all-reflective instrument with 14 mirrors, 7 interchangeable filters, and an opaque shutter that can be combined with 7 interchangeable dispersers and a plane mirror.
On this page
JWST instruments share a focal plane, shown in Figure 1. NIRSpec is on the left, with an aperture position angle rotated approximately 138.5° counter-clockwise relative to the +V3 axis. JWST's other near-infrared instruments have coordinate axes that are roughly aligned with the V2 and V3 coordinates (shown at center right). The 4 quadrants of the micro-shutter assembly (MSA) are highlighted, along with the small apertures for the integral field unit (IFU) and fixed slits (FSs). The dimensions of the quadrants and gaps are labeled. The faint blue streaks depict example spectra from the MSA and FSs and indicate the dispersion direction of NIRSpec.
NIRSpec optical path
NIRSpec is an all-reflective instrument with 14 mirrors, 7 interchangeable filters and an opaque option in the filter wheel assembly (FWA), 7 interchangeable dispersive elements, and a plane mirror in the grating wheel assembly (GWA).
Its optical path starts with the coupling optics. These are followed by 3 major optical subsystems: the fore optics (FORE), the collimator optics (COLL), and the camera optics (CAM). Each are implemented as a 3-mirror anastigmat (TMA) to minimize optical aberrations.
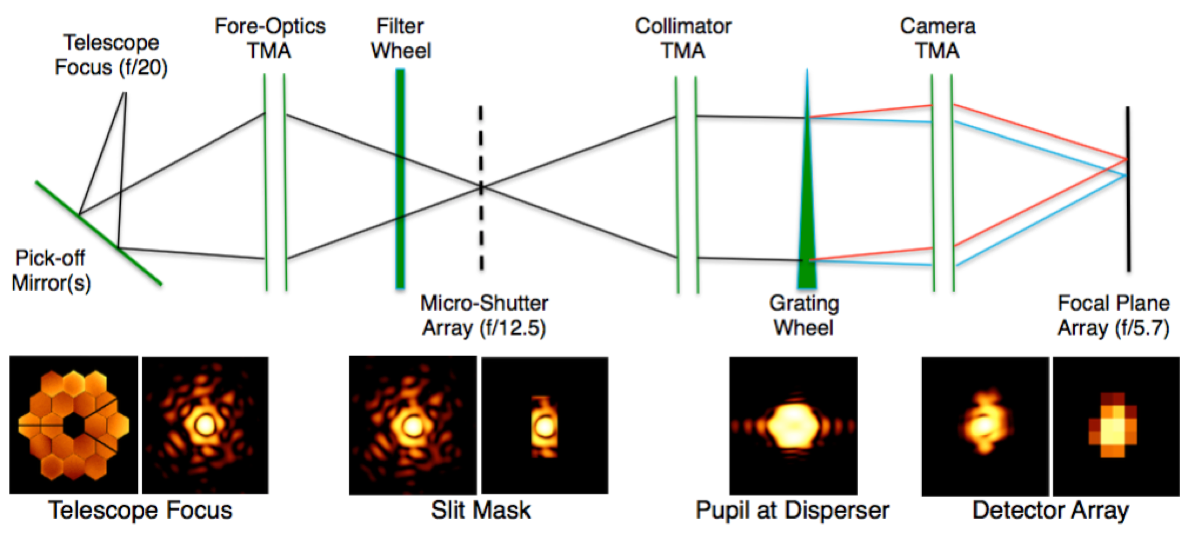
There are 3 pupil planes and 3 image planes in the optical path, as shown in Figure 2. The pupil planes are located at the Optical Telescope Element (OTE) primary mirror, the FWA, and the GWA. The 3 image planes are located at the OTE focal plane, the aperture plane, and the focal plane assembly (FPA), where the detectors are located. Figure 2 also shows an estimate of how optical distortions can affect the point spread function (PSF) image shape at different points along the optical path. Figure 3 shows the optical path by itself, and Figure 4 depicts the optical path within NIRSpec.
Additional IFU-specific optics are detailed in the NIRSpec Integral Field Unit article.
A schematic of the NIRSpec optical path, with the major optical elements labeled. At the different pupil and focal planes, a modeled image of a star is shown in the lower panel, presenting estimated distortion to a point spread function (PSF) at different points through the optical path.
Coupling optics
The coupling optics consist of 2 flat mirrors that pick off the NIRSpec portion of the OTE focal plane and redirect it into the fore optics. The first coupling mirror—also referred to as a pick-off mirror (POM)—has a field mask in front of it. The field mask, together with a closed optical base plate structure and an internal pupil mask, minimize the amount of out-of-field stray light entering the diverging OTE beam.
Fore optics (FORE), filter wheel assembly (FWA), and refocus mechanism assembly (RMA)
The fore optics are the first TMA system. It re-images a portion of the curved OTE focal surface through the FWA and onto the flat aperture plane, where the micro-shutter assembly (MSA), integral field unit (IFU), and fixed slits (FSs) apertures are located. At the FWA, the beam is nearly collimated and has a small incidence angle in order to avoid optical ghosting. This small angle offset creates a tilt of the resultant spectra on the detector.
One position in the FWA, OPAQUE, is used as an instrument shutter. It blocks light from entering NIRSpec for dark measurements and whenever NIRSpec is not being used. The inward-facing side of the OPAQUE position has a concave mirror that reflects light into the optical path from the calibration lamps. The skyward-facing side of OPAQUE is also reflective in order to minimize the stray light within NIRSpec's fore optics.
The refocus mechanism assembly (RMA) can be used to adjust the exact position along the optical axis at which the focal plane is re-imaged onto the aperture plane, thus compensating for any changes in the OTE focus position that may occur during launch and throughout the JWST lifetime.
Collimator optics (COLL) and grating wheel assembly (GWA)
After passing through the aperture plane, the optical beam enters NIRSpec's second TMA system, the collimator optics. These optics transform the divergent beam from the aperture plane into a highly collimated beam before passing the light to the GWA.
Camera optics (CAM) and focal plane assembly (FPA)
After being dispersed or reflected by an optical element in the GWA, the NIRSpec beam enters the camera (CAM), the third and final TMA. These CAM optics focus the collimated and dispersed beam onto the FPA, which contains 2 closely spaced detectors.
Note that the exact plate scale varies over the field because of the optical distortions caused by the OTE and the TMAs.
References
Dorner, B., Giardino, G., Ferruit, et al. 2016, A&A 592, A113
A model-based approach to the spatial and spectral calibration of NIRSpec onboard JWST