Step-by-Step ETC Guide for NIRSpec MOS Deep Extragalactic Survey
This is a JWST NIRSpec MOS deep extragalactic survey example science program. The ETC step-by-step instructions are provided in detail here.
Example Science Program #25 ETC Guide
Dated material
This example was created pre-launch, and the ETC has been updated since its creation. You may see differences in the details of the results from the ETC, the information provided, or the appearance of the ETC GUI from what is shown herein.
Please refer to JWST Example Science Programs for more information.
On this page
See also: NIRSpec Multi-Object Spectroscopy, JWST Exposure Time Calculator Overview, Proposal Planning Video Tutorials
Exposure time calculations
Words in bold are GUI menus/
panels or data software packages;
bold italics are buttons in GUI
tools or package parameters.
The optimal exposure specifications (e.g., number of groups and integrations) are the input needed for the Astronomer's Proposal Tool (APT) observation template, which is used to specify an observing program and submit proposals.
The ETC workbook associated with this Example Science Program is called "#25 NIRSpec MOS Deep Extragalactic Survey" and can be selected from the Get a Copy of an Example Science Program dropdown on the ETC Workbooks page to get the read only version. The nomenclature and reported SNR values in this article are based on ETC v. 1.5.1. There may be subtle differences if using a different version of ETC.
Define Sources and Scenes in the ETC
See also: JWST ETC Scenes and Sources Page Overview
As stated above, our goals are to measure the [CIII], CIII], and Hα emission lines with a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of 5. We set up sources in the ETC to have continuum levels representative of the brightest 5 < z < 6 galaxies in our catalog, as shown in Table 1. We define the sources as extended, assuming a 2D Gaussian with semi-major and semi-minor axes of 0.17 arcseconds. This corresponds to 1 kpc at a redshift of z = 5.5, a typical size for galaxies at this redshift (Curtis-Lake et al. 2016.) Each scene has one source assigned to it, at the center of the scene, so that in the calculations below, we assume the sources are centered in the spectroscopic slit.
| Scene Number | Scene Name | Source Name | Continuum | Shape |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C III] Scene | C III] Calculation | SED: Flat in Fν Normalization:
| Extended 2D Gaussian, integrated flux σx = σx = 0.17 arcsec |
| 2 | Hα Scene | Hα Calculation | SED: Flat in Fν Normalization:
| Extended 2D Gaussian, integrated flux σx = σx = 0.17 arcsec |
As of ETC v. 1.5.1, the continuum-subtracted SNR of an emission line is not provided. The ETC instead reports the SNR per pixel. Below, we describe how we estimate an appropriate SNR per pixel for our science goals, by estimating the expected fluxes of the emission lines of interest, determining the SNR of a continuum subtracted line, and translating this information to SNR per continuum pixel.
Estimating expected fluxes of the emission lines of interest
We estimate the expected flux of [CIII], CIII], using equivalent width measurements in the literature, along with a WFC3 IR F140W magnitude of 26 AB, representative of the brightest 5 < z < 6 galaxies in our catalog.
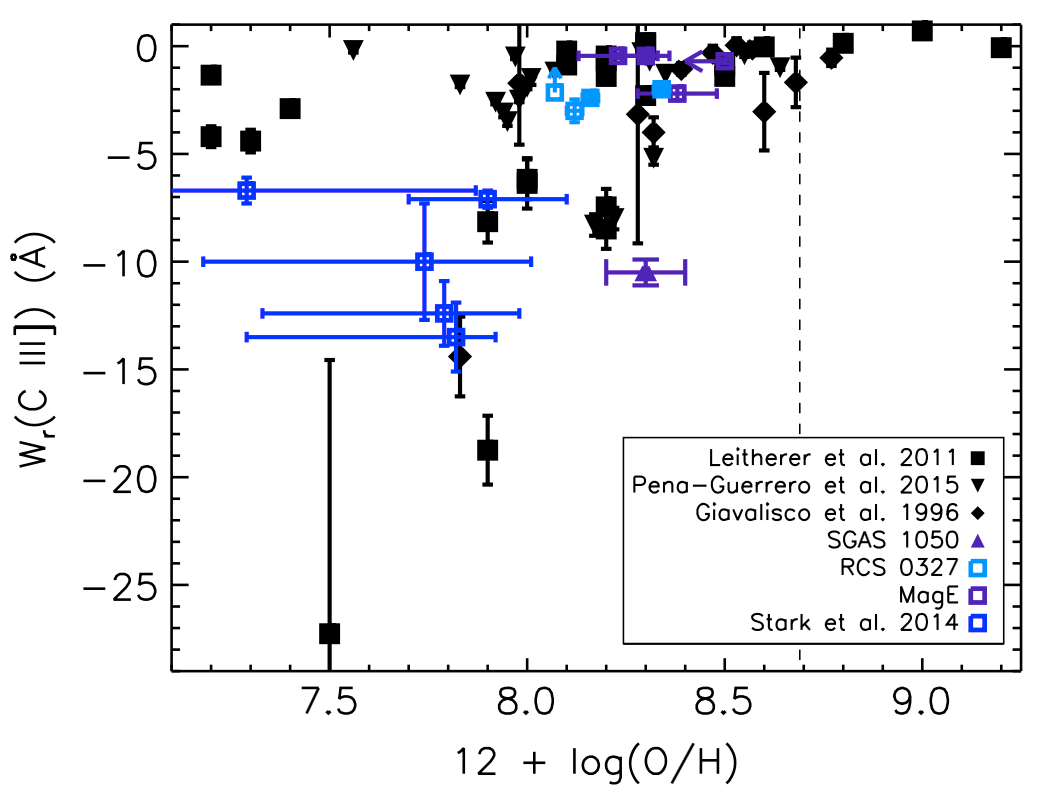
To obtain a typical equivalent width, we look to Figure 1 which is from Rigby et al. 2015. From this figure, we infer that an equivalent width of 10 Å is typical of galaxies with the low metallicities that we may expect at these redshifts. Given these numbers, we estimate that we must reach a flux of 1.5x10-18 ergs s-1 cm-2 (assuming a redshift of z = 5.5). Additionally, we wish to measure star-formation rates down to 1 solar mass per year which corresponds to an Hα flux of 3.8x10-18 ergs s-1 cm-2 at a redshift of 6.
Estimating SNR for a continuum-subtracted line
We need to perform continuum subtraction to obtain flux measurements from our emission lines. Therefore, we need to perform an exposure time calculation for a continuum-subtracted line. To do so, we use a combination of JWST ETC calculations and our own custom model, which is provided as an Python notebook in the next section.
The JWST ETC returns SNR per pixel for the entire spectrum of an input source. Our simple model translates this to a SNR integrated over a continuum-subtracted emission line.
The model consists of a Monte-Carlo simulation where we add differing amounts of noise to a model galaxy spectrum. We then mock observe the line of interest for each Monte-Carlo realization and determine its SNR. Figure 2 shows an example simulated 1D spectrum from our study.
For Hα, we ran the model for an input spectrum with a continuum magnitude of 27 in WFC3/F160W (typical of the highest redshift sources in our catalog) and a line flux of 3.8 x 10-18 ergs s-1 cm-2. Again, the line is assumed to be a Gaussian having a width that is the same as the spectral resolution element. By iterating on the continuum S/N, we find that a value of 0.12 per pixel is required to measure Hα with a SNR of 5 in the line.
Model to estimate SNR for a continuum-subtracted line
The details of our simple model to estimate SNR for a continuum-subtracted emission line are as follows.
The model is available as a Python notebook. First, we start by creating a noise-free model spectrum (line + continuum). Then, we choose a root-mean-square (RMS) for the error spectrum, that will yield a fixed continuum SNR. For each model spectrum we:
- Monte Carlo 5000 noise spectra with the same RMS,
- add these spectra to the noise-free model,
- mock observe the resulting spectra, and
- calculate the RMS of the mock observations of the line and convert it into a SNR by dividing the input flux by this rms.
This results in a SNR measurement for a line, given the SNR on the continuum. We then iterate to determine the continuum SNR that will yield a line SNR of 5. In this model, it is assumed that noise does not vary with wavelength in the vicinity of the line. This is because the lines are faint enough that the Poisson noise from the source is negligible. Note that for [CIII], CIII], both lines in the doublet are simulated, but are blended. For Hα only a single line is simulated.
For [CIII], CIII] and Hα we want a S/N of 5 in the line. This requires a SNR of 1.25 per pixel in G140M/F100LP for a source with 26th magnitude in WFC3 IR F140W, and a SNR of 0.12 per pixel in G235M/F170LP and G395M/F290LP for a source with 27th magnitude (AB).
Run ETC calculations for NIRSpec multi-object spectroscopy
See also: JWST ETC Calculations Page Overview
In the Calculations tab of the ETC, we choose the Multi-Object Spectroscopy option in the NIRSpec pull-down menu.
For the CIII] calculation (Calculation #3), we populated the "Instrument Setup" tab as follows. We chose G140M/F100LP grating/filter combination to cover the [CIII], CIII] line at redshifts 5 < z < 6. We chose the default 3-shutter slitlet, which corresponds to the design that we implement. We also leave the MSA location at the default (Quad 3 center); in practice this choice makes little difference in sensitivity, but it does give different estimates for wavelength gaps and cutoffs, which vary with location on the MSA.
In the Strategy tab, we select a “wavelength of Interest” of 1.25 μm, which is near the observed wavelength of [CIII], CIII] at a redshift of z = 5.5.
On the Detector Setup tab, we use the NRSIRS2 detector readout pattern, which reduces correlated noise and is recommended for long exposures. We find that 20 groups, 10 integrations, and 3 exposures, are optimal, totaling 12 hours and 16 minutes. Here, the three exposures are used to model the three nod positions in the MOS observations. The choice of 20 groups gives ramps of 1473s, below the recommended ~1500 second maximum set by the rate of cosmic rays. However, with this choice of exposure parameters, we find that each nod would have more than 14,000 seconds of exposure, longer than JWST’s maximum allowed exposure time of 10,000 seconds.
Therefore, we must break these exposures into two. Hence, in the ETC we conclude that 20 groups, 5 integrations, and 6 exposures will meet our SNR goal. This calculation can be found as ID #3 in the ETC workbook for this example science program (#25).
We run two calculations for the Hα emission line: one for G235M/F170LP at a "wavelength of interest" of 2 μm (Calculation #4) and another for G395M/F290LP at a "wavelength of interest" at 4 μm (Calculation #5), again, using the NRSIRS2 readout pattern. In order to reach a continuum S/N of 0.12, we find that 15 groups, 1 integration, and 3 exposures (3326 seconds) are required for both G235M/F170LP and G395/F290LP.
References
Curtis-Lake, E., et al. 2016, MNRAS, 457, 1, 440
Non-parameteric analysis of rest-frame UV sizes and morphological disturbance amongst L* galaxies at 4 < z < 8
Grogin, N.,et al. 2011, ApJS, 197, 2, 35
CANDELS: The Cosmic Assembly Near-infrared Deep Extragalactic Legacy Survey
Momcheva, I. G., et al. 2016, ApJS, 225, 2, 27
The 3D-HST Survey: Hubble Space Telescope WFC3/G141 Grism Spectra, Redshifts, and Emission Line Measurements for ~100,000 Galaxies
Rigby, J. R., et al. 2015, ApJL, 814, 1, L6
C III] Emission in Star-forming Galaxies Near and Far
Tremonti, C. A., et al. 2004, ApJ, 613, 2, 898
The Origin of the Mass-Metallicity Relation: Insights from 53,000 Star-forming Galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey