NIRCam Pupil and Filter Wheels
The JWST NIRCam pupil and filter wheels include the filters, weak lenses, grisms, and coronagraph Lyot stops that may be used in combination.
On this page
Each NIRCam module has short wavelength (0.6–2.3 μm) and long wavelength (2.4–5.0 μm) channels, each with a pupil wheel and filter wheel of 12 elements each. Many combinations of pupil and filter wheel elements are allowed as described below. These elements include:
- extra-wide-, wide-, medium-, and narrowband filters with R = λ/Δλ ~ 1, 4, 10, and 100, respectively;
- coronagraph Lyot stops to suppress diffracted light that passes the occulting masks on the focal plane;
- grism elements in the long wavelength channel—2 elements are available, dispersing light along detector rows and columns, respectively;
- weak lenses to defocus light from bright sources to avoid detector saturation, and also used for telescope alignment;
- clear positions (empty holes) in the pupil wheel to be used in combination with filter wheel elements;
- dark elements used for calibration;
- other elements used only for wavefront sensing and telescope alignment, including the PAPPA (pupil alignment pinhole projector assembly), DHS (dispersed Hartman sensing), and IPR Wedge (internal phase retrieval).
Pupil and filter wheels characteristics
Table 1. NIRCam pupil and filter wheel elements
Short wavelength channel | Long wavelength channel | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table notes:
Black: bandpass filters named W2, W, M, N have R = λ/Δλ ~ 1, 4, 10, 100, respectively
Orange: coronagraphic Lyot stops in the pupil wheels used in conjunction with filters and focal plane occulting masks
Green: grism elements disperse spectra along detector rows (R) or columns (C), used in conjunction with filters
Magenta: WL, weak lens, used to defocus for mirror alignment or bright star imaging without saturation
Gray: CLEAR positions, empty holes in the pupil wheel
Wavefront sensing/calibration (not available for science)
DHS, dispersed Hartman sensing (sub-aperture grisms): coarse phasing alignment of JWST's mirrors
PAPPA, pupil alignment pinhole projector assembly: align NIRCam with the JWST Optical Telescope Element (OTE)
IPR, internal phase retrieval, wedge: measure NIRCam wavefront errors using LEDs mounted on coronagraphs
Dark: blocks incoming light for dark current measurements
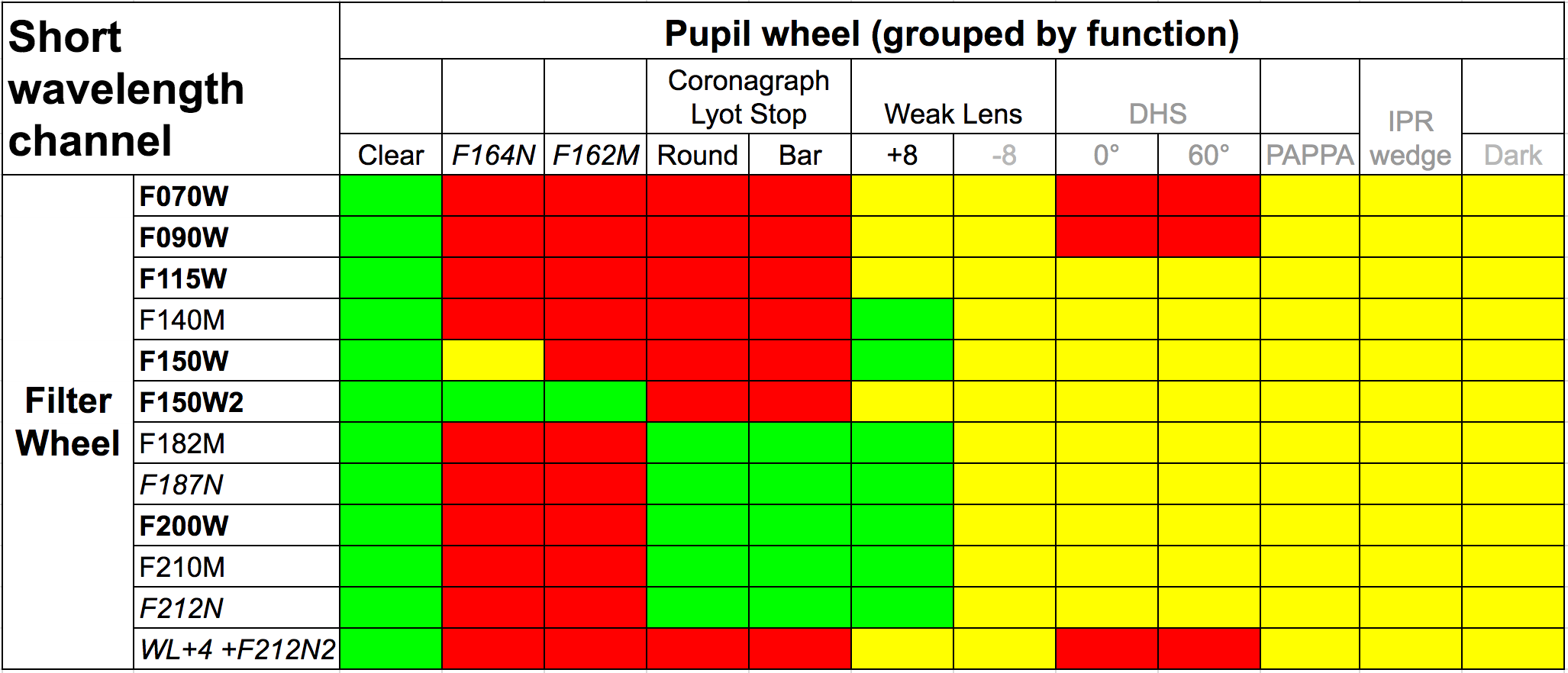
Allowed combinations between pupil and filter wheel elements
Pair availability
- Green: available for science
- Yellow: restricted use for wavefront sensing, calibration, or engineering
- Red: disallowed; not useful
Names of wide, medium, and narrow filters are formatted as bold, regular, and italic, respectively.
- Starting in Cycle 2, simultaneous short wavelength (SW) and long wavelength (LW) coronagraphy is available. All LW medium, wide, and W2 filters are available for use with MASKSWB. The same LW filters are available for MASK210R, with the exception of F277W.
Available pupil and filter wheel pairings for the long wavelength channel. Same color codes as Figure 2.
- Green: available for science
- Yellow: restricted use for wavefront sensing, calibration, or engineering
- Red: disallowed; not useful
Names of wide, medium, and narrow filters are formatted as bold, regular, and italic, respectively.
335, 430: the filters allowed in combination with a round coronagraph Lyot stop depend on the occulting mask used: MASK335R or MASK430R.
- Starting in Cycle 2, simultaneous short wavelength (SW) and long wavelength (LW) coronagraphy is available. For all three LW masks, F182M, F210M, F187N, F212N, and F200W are available to select in the SW channel.
Words in bold are GUI menus/
panels or data software packages;
bold italics are buttons in GUI
tools or package parameters.