Pandeia Reports
A description of the structure and content of JWST Pandeia output reports is provided in this article.
On this page
Pandeia can produce 2 possible outputs from run_calculation.
If the command is run as "perform_calculation(<configuration>, dict_report=True)", (or simply as "perform_calculation(<configuration>)"), since "dict_report" defaults to True), it will return a dictionary with various information about the calculation inputs and results.
If, instead, the command is run as "perform_calculation(<configuration>, dict_report=False)", it will return a "pandeia.engine.Report" object, which will have the same information available, and which can output a dictionary (with exactly the same contents as if "dict_report" had been set to true) via the "as_dict()" method. In general, the dictionary report is recommended unless there some specific output information is desired but not obtainable from the dictionary (see below for examples of this).
Pandeia report dictionary structure
The pandeia report dictionary contains the following keys and content:
sub_reports: list, containing information on each exposure for multiple exposures (e.g., IFU dither patterns or coronagraphic imaging). Each report in thesub_reportslist will be in the same format as a standard dictionary report.information: dictionary, containing information on the exposure specifications that Pandeia used to generate its result. It contains:calc_type: string, the type of 2D projection performed. One ofslitless,multiorder,image,specexposure_specification: dictionary. Contains information on how the exposure was conducted and the assumed telescope and instrument status. Contains the following:exposure_time: floating point, exposure time for each exposure (sec)total_exposure_time: floating point, total time spent observing the target; equal toexposure_timemultiplied by the number of exposures (sec)measurement_time: floating point, time between the first and last measurements of a pixel in an integration multiplied by the number of integrations per exposure (sec)saturation_time: floating point, time from the reset of a pixel to the final read of that pixel in an integration multiplied by the number of integrations per exposure (sec)duty_cycle: floating point, the fraction of the exposure time that was devoted to observing the target;duty_cycle= measurement_time/exposure_timenexp: integer, number of exposuresnframe: integer, number of frames per grouptframe: floating point, time per frame (sec)nskip: integer, number of skipped frames per group; only supported by some readout patternsframe0: boolean, whether the first frame was downlinked and used in the ramp fit; applies only to NIRCamngroup: integer, number of groups per integrationtgroup: floating point, telescope time per group (sec)nprerej: integer, either0or1(default0); applies only to MIRI; number of groups at the beginning of the ramp that were rejected by the pipelinenint: integer, number of integrations per exposure- npostrej: integer, either 0 or 1 (default 0); applies only to MIRI; number of groups at the end of the ramp that were rejected by the pipeline
total_integrations: integer, number of integrations in all exposures combinednramps: integer, total number of ramps in the observation;nrampsis equal tonintmultiplied by the number of exposuresreadout_pattern: string, name of the readout patternsubarray: string, name of subarray used for the exposuredet_type: string, type of detector involved (e.g., 'h2rg' for NIRCam short wavelength detectors)nsample: integer, number of samples averaged when reading a single pixel; applies only to MIRItsample: floating point, time averaged when reading a single pixel; applies only to MIRI (sec)nsample_skip: integer, number of samples skipped while reading a single pixel; applies only to MIRInsample_total: integer, total number of samplestfffr: integer, extra time for full frame resets (sec)
warnings: dictionary, contains all warnings generated by the exposure. Warnings can include:- <instrument>
_missing_instrument_aperture: generated if the supplied configuration dictionary did not include the aperture information; the warning text will indicate what the aperture has been set to partial_saturated: indicates partial saturation of at least one pixel; the warning text will include the number of partially saturated pixelsfull_saturated: indicates full (unrecoverable) saturation of at least one pixel; the warning text will include the number of fully saturated pixels
- <instrument>
transform: dictionary, containing the coordinate transform information that describes the image axes for the 2-D and 3-D data. Contains the following values:wave_refpix: integer, the reference pixel of the wavelength arrays (pixels)wave_refval: floating point, the value ofwave_refpix(μm)wave_step: floating point, interval between successive points in the wavelength array (μm)wave_size: integer, the size of the wavelength axis (pixels)wave_min: floating point, the minimum wavelength value of the 2-D and 3-D data (μm)wave_max: floating point, maximum wavelength of the 2-D and 3-D data (μm)x_refpix: integer, the reference pixel for the x-axis in the 2-D and 3-D data (pixels)x_refval: floating point, the value of thex_refpixpixel of the x-axis of the 2-D and 3-D data (arcsec)x_step: the per-pixel size of the x-axis of the 2-D and 3-D data (arcsec)x_size: integer, the size of the x-axis of the 2-D and 3-D data supplied in the report (pixels)x_min: floating point, the minimum value of the x-axis of the 2-D and 3-D data (arcsec)x_max: floating point, the maximum value of the x-axis of the 2-D and 3-D data (arcsec)y_refpix: integer, the reference pixel for the y axis in the 2-D and 3-D data (pixels)y_refval: floating point, the value of they_refpixpixel of the y axis of the 2-D and 3-D data (arcsec)y_step: floating point, the per-pixel size of the y-axis of the 2-D and 3-D data (arcsec)y_size: integer, the size of the y-axis in the 2-D and 3-D data (pixels)y_min: floating point, the minimum value of the y-axis in the 2-D and 3-D data (arcsec)y_max: floating point, the maximum value of the x-axis in the 2-D and 3-D data (arcsec)wave_det_refpix: integer, the detector reference pixel in wavelength space (if applicable) (pixels)wave_det_refval: floating point, the value ofwave_refpixon the detector (if applicable) (μm)wave_det_step: floating point, the distance in wavelength space between adjacent pixels on the detector (if applicable) (μm)wave_det_size: integer, the length of the wavelength axis of the detector (pixels)wave_det_min: floating point, the minimum wavelength value of the detector (μm)wave_det_max: floating point, the maximum wavelength value of the detector (μm)
scalar: dictionary, contains scalar values of interest from the observation. Includes the following values:exposure_time: floating point, the same value asexposure_timein the 'information:exposure_specification' part of the report (sec)aperture_size: floating point, size of the extraction aperture (arcsec)cr_ramp_rate: floating point, expected cosmic ray events per pixel per ramp (events/sec/pixel)reference_wavelength: floating point, wavelength used for determining scalar outputs (μm)extraction_area: floating points, area (in square arcseconds) from which data is extracted for scalar outputs (arcsec2)all_dithers_time: floating point, total time (in seconds) spent during the observation during all exposures/dithers, whether on-target or off-target (sec)total_integrations: integer, the same value astotal_integrationsin the 'information:exposure_specification' part of the reportsaturation_time: floating point, the same value assaturation_timein the 'information:exposure_specification' part of the report (sec)measurement_time: floating point, the same value asmeasurement_timein the 'information:exposure_specification' part of the report (sec)fraction_saturation: floating point, the fraction describing how close to saturation the brightest pixel on the detector isdetector_ngroups: integer, the maximum number of groups that can be requested before the brightest pixel on the detector saturatessn: floating point, signal-to-noise ratio for the observationextracted_noise: floating point, total noise counts extracted in the background region (e–/sec)extracted_flux: floating point, total flux extracted from the extraction aperture (e–/sec)brightest_pixel: floating point, rate of brightest pixel on the 2-D image (e–/sec)duty_cycle: floating point, the same value asduty_cyclein the 'information:exposure_specification' part of the reportbackground: floating point, flux of the background spectrum at the reference wavelength (MJy/sr)contamination: floating point, flux from contamination by other (non-target) sources in the background region (e–/sec)background_sky: floating point, flux in the background extraction region contributed by the sky (e–/sec)disperser: string, the grating/prism/grism in use, if anyfilter: string, the filter in use, if anyy_offset: floating point, the y-offset of the target (arcsec)x_offset: floating point, the x-offset of the target (arcsec)background_area: floating point, the background extraction area (arcsec2)background_total: floating point, the background flux including both sky and contamination (e–/sec)total_exposure_time: floating point, the same value astotal_exposure_timein the 'information:exposure_specification' part of the report (sec)
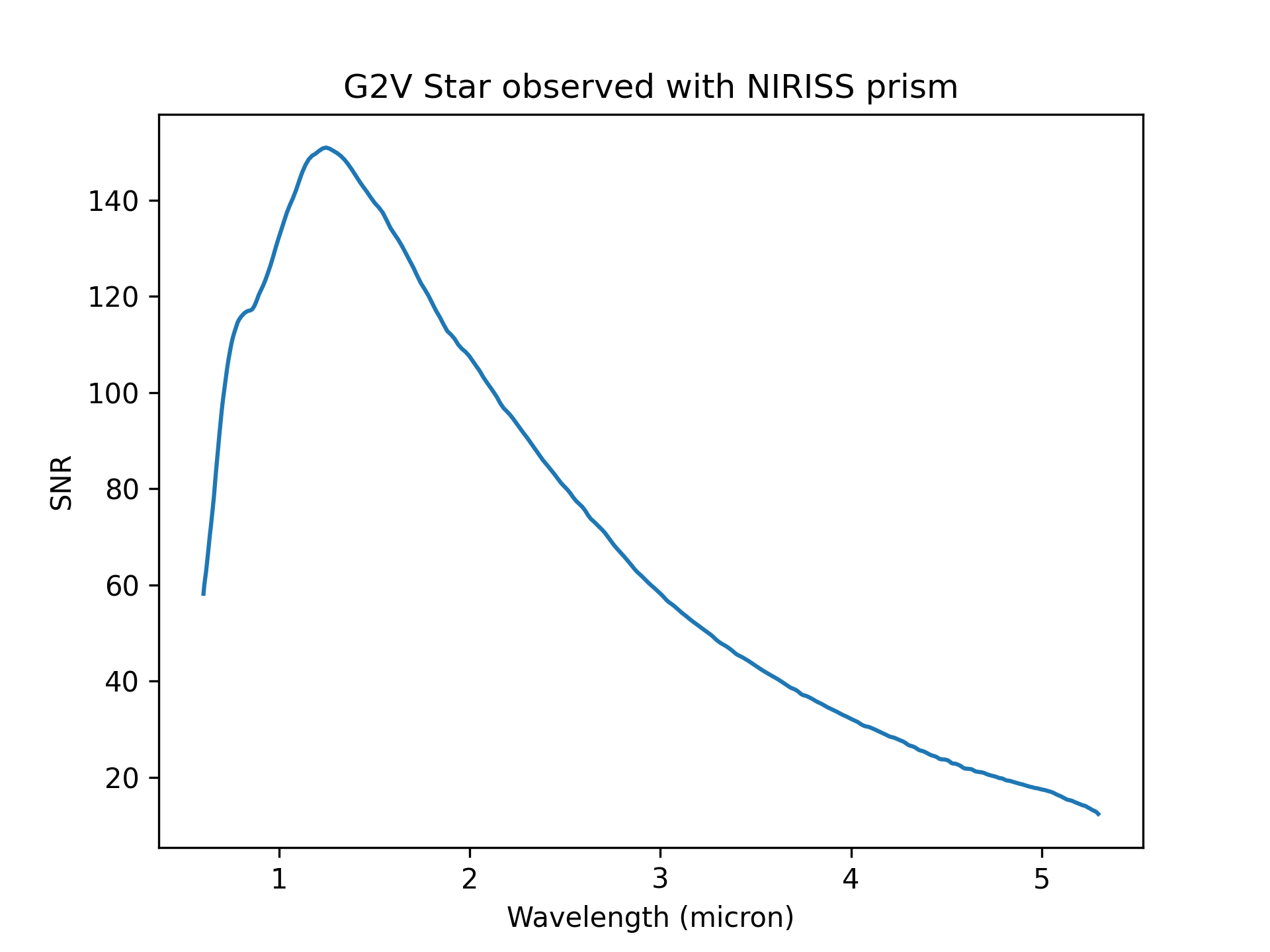
1d: dictionary, Contains 1-D spectra representing various aspects of the observation, presented either as a function of wavelength or alongside the reference wavelength. In the descriptions below, names in italics are single values presented against the reference wavelength if the calculation is an 'imaging' calculation. Values include:fp: count rate at the focal plane (μm, e–/sec)extracted_contamination: flux from contamination (μm, e–/sec)total_flux: combined target and background flux (μm, e–/sec)bg: background flux (μm, MJy/sr)extracted_noise: standard deviation of the extracted flux (μm, e–/sec)bg_rate: background flux at the focal plane (μm, e–/sec)extracted_bg_only: extracted background flux not including contamination (if any) (μm, e–/sec)n_partial_saturated: number of partially saturated pixels (μm, unitless)n_full_saturated: number of fully saturated pixels (μm, unitless)sn: signal-to-noise ratio (μm, unitless)wave_pix: single array containing the reference wavelength as its only value (μm)extracted_flux: total extracted flux from the target (μm, e–/sec)extracted_flux_plus_bg: total countrate including both target and background (μm, e–/sec)wave_calc: single array containing the wavelengths over which the exposure was calculated (μm)extracted_bg_total: total extracted background flux (μm, e–/sec)target: target flux as a function of wavelength (μm, e–/sec)
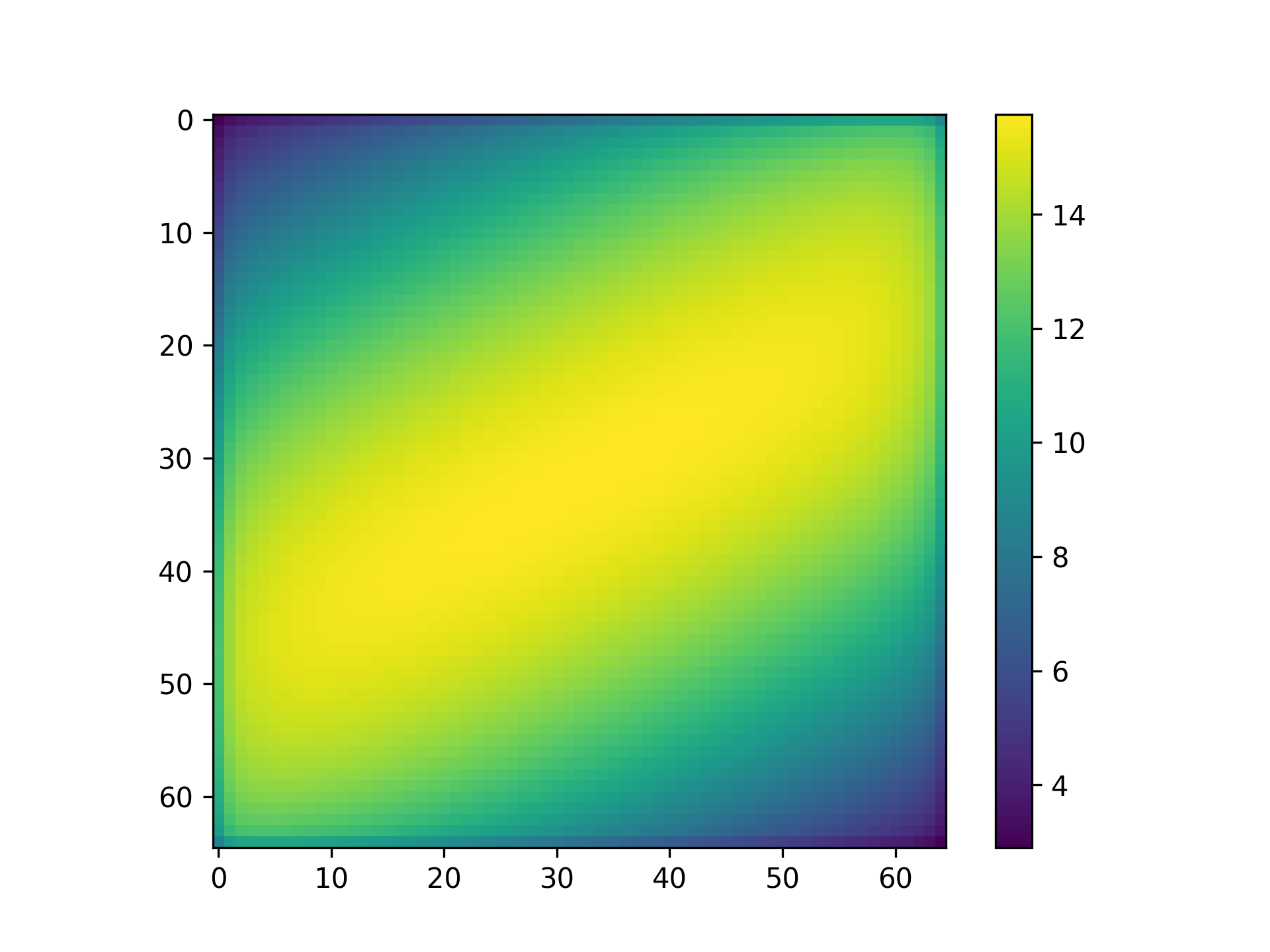
2d: dictionary, contains 2-D images of the on-detector observation. Values include:snr: 2-D NumPy array of floating point values, the signal-to-noise ratio for each pixel in the observationdetector: 2-D NumPy array of floating point values, the on-detector countrate for each pixel in the observation (e–/s)saturation: 2-D NumPy array of floating point values, the detector saturation information; pixels have the value of 0 (unsaturated), 1 (partial saturation), or 2 (full saturation)ngroups_map: 2-D NumPy array of integer values, the maximum number of groups before a given pixel on the detector would saturate
3d: dictionary, contains 3-D data cubes of the on-detector observations. Available only for MIRI MRS, MIRI MRS Time Series, and NIRSpec IFU. Values include:flux: 3-D NumPy array of floating point values, contains flux as a function of wavelength for each pixel at each wavelength in Pandeia's internal observation measurement (μm, e–/s)flux_plus_background: 3-D NumPy array of floating point values, contains flux and background together for each pixel at each wavelength (μm, e–/s)
input: dictionary, containing information about the calculation inputs. When running Pandeia from Python, this should simply be a copy of the configuration dictionary (see Pandeia Configuration Dictionaries for more information on the configuration dictionary). As such, its contents will not be further discussed here.
Pandeia report fits object
Pandeia can also output a dictionary of FITS objects, by outputting a report object (created by running "perform_calculation(<configuration>, dict_report=False)" and running the 'as_fits()' method on the resulting Report object)
1d: dictionary, with a FITS HDU list for every item in the regular 1-D report dictionary mentioned above. All of the FITS headers except wave_calc and wave_pix will have 2 fields in the first header: wavelength (either wave_calc or wave_pix) and the property in question.2d: dictionary, with a FITS HDU list for every item in the regular 2-D report dictionary. All of the FITS headers have WCS information extracted from the detector pixel grid. These headers are, for 2-D spectroscopic modes, assumed to be linear wavelength scales; it may be necessary to use the 1-D wave_calc value to generate accurate wavelengths.3d: dictionary, with a FITS HDU list for every item in the regular 3-D report dictionary. All of the FITS headers have WCS information extracted from the detector pixel grid. These headers are assumed to be linear in wavelength scale; it may be necessary to use the 1-D wave_calc values to generate accurate wavelengths.
Pandeia report object
The pandeia 'Report' object contains the same data as the report dictionary (and can be converted into the report dictionary via its 'as_dict()' method, or fits dictionary via its 'as_fits()' method), but also contains some additional information.
Per-pixel background count rate
The Pandeia Report object stores the per-pixel background count rate in the internal property 'bg_pix'. This contains a 2-D array of the entire simulated region of the detector with the per-pixel sky background for each pixel, and could potentially be useful in determining background flux in order to compare observations when looking for the lowest possible background.
Interpreting downloads from the JWST ETC website
When running simulations on the JWST ETC website, you can download the result of a particular simulation. In addition to the input values used for the simulation (discussed in the Pandeia Quickstart, the download also contains many FITS files which provide information about the simulation, and which often correspond to the content of a Pandeia report.
Structure of a JWST ETC result download
JWST ETC downloads contain the following files and folders. Note that these files are also discussed on the JWST ETC Downloads page.
- "backgrounds.fits": FITS file containing the spectrum used to determine background count rates
- cube (non-IFU observations)
- cube_flux_plus_background.fits
- cube_flux.fits
- model (empty folder)
- cube (IFU observations)
- cube_reconstructed.fits
- cube_reconstructed_noise.fits
- cube_reconstructed_snr.fits
- cube_reconstructed_saturation.fits
- cube_reconstructed_signal.fits
- model
- cube_flux_n.fits (one for each IFU element, with the n replaced by the element number)
- cube_flux_plus_background_n.fits (one for each IFU element, with the n replaced by the element number)
- image
- image_detector.fits
- image_ngroups_map.fits
- image_saturation.fits
- image_snr.fits
- input.json (discussed in the Pandeia Quickstart)
- lineplot
- lineplot_bg_rate.fits
- lineplot_bg.fits
- lineplot_extracted_bg_only.fits
- lineplot_extracted_bg_total.fits
- lineplot_extracted_contamination.fits
- lineplot_extracted_flux_plus_bg.fits
- lineplot_extracted_flux.fits
- lineplot_extracted_noise.fits
- lineplot_fp.fits
- lineplot_n_full_saturated.fits
- lineplot_n_partial_saturated.fits
- lineplot_sn.fits
- lineplot_target.fits
- lineplot_total_flux.fits
- lineplot_wave_calc.fits
- lineplot_wave_pix.fits
Accessing downloaded FITS files
FITS files are most easily accessed via the AstroPy module, in particular "astropy.io.fits". Below is an example of obtaining data from a lineplot file, assuming that Python is run from the base directory of the download.
import astropy.io.fits as f
with f.open('lineplot/lineplot_extracted_bg_total.fits') as input_file:
reference_wavelength = input_file[1].data[0]['WAVELENGTH']
extracted_flux = input_file[1].data[0]['extracted_bg_total']
Correspondences with the Pandeia report dictionary
| File | Extension | Equivalent Key |
|---|---|---|
| cube/cube_flux_plus_background.fits | 0 | report['3d']['flux_plus_background'] |
| cube/cube_flux.fits | 0 | report['3d']['flux'] |
| image/image_detector.fits | 0 | report['2d']['detector'] |
| image/image_saturation.fits | 0 | report['2d']['saturation'] |
| image/image_snr.fits | 0 | report['2d']['snr'] |
| image/image_ngroups_map.fits | 0 | report['2d']['ngroups_map'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_bg_rate.fits | 1 | report['1d']['bg_rate'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_bg.fits | 1 | report['1d']['bg'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_extracted_bg_only.fits | 1 | report['1d']['extracted_bg_only'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_extracted_bg_total.fits | 1 | report['1d']['extracted_bg_total'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_extracted_contamination.fits | 1 | report['scalar']['contamination'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_extracted_flux_plus_bg.fits | 1 | report['1d']['extracted_flux_plus_bg'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_extracted_flux.fits | 1 | report['1d']['extracted_flux'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_extracted_noise.fits | 1 | report['1d']['extracted_noise'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_fp.fits | 1 | report['1d']['fp'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_n_full_saturated.fits | 1 | report['1d']['n_full_saturated'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_n_partial_saturated.fits | 1 | report['1d']['n_partial_saturated'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_sn.fits | 1 | report['1d']['sn'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_target.fits | 1 | report['1d']['target'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_total_flux.fits | 1 | report['1d']['total_flux'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_wave_calc.fits | 1 | report['1d']['wave_calc'] |
| lineplot/lineplot_wave_pix.fits | 1 | report['1d']['wave_pix'] |
Downloaded background file
The "backgrounds.fits" file included in the download contains a data table in its first extension. This table includes the following columns:
- wavelength: the wavelength in μm
- background: total background flux
- thermal: the thermal component of the total background flux
- straylight: the stray light component of the background flux
- infield: the sky component of the background flux
Sample code
Displaying an image of the signal-to-noise ratio of a Pandeia imaging observation
Note that the above is being done in a very simplistic way, and that Matplotlib, in particular, has many options that aren't on display here. See the matplotlib user's guide for many more details.
Displaying the signal-to-noise ratio of a spectrum as a function of wavelength