NIRSpec Dispersers and Filters
JWST's NIRSpec has 7 filters covering the 0.6–5.3 μm wavelength region and 7 dispersive elements that include 6 gratings and a prism. These filters and dispersive elements are combined to take spectra in the NIR region.
On this page
NIRSpec is sensitive to nearly a full decade in wavelength: 0.6–5.3 µm. The NIRSpec optical path contains 2 wheel mechanisms, the grating wheel assembly (GWA) and the filter wheel assembly (FWA), which provide disperser-filter combinations to cover the NIRSpec wavelength range. The NIRSpec dispersers and filters form matched sets to cover the wavelength ranges shown in Figure 1, with one configuration in low spectral resolution mode (R ~ 30–300), and 4 configurations in medium (R ~ 1,000) and high (R ~ 2,700) spectral resolution mode.
The FWA contains 7 transmission filters, plus an OPAQUE position. The GWA contains 6 diffraction gratings, a double-pass prism, and a flat mirror.
NIRSpec filters
Words in bold are GUI menus/
panels or data software packages;
bold italics are buttons in GUI
tools or package parameters.
There is also an 8th NIRSpec FWA position, OPAQUE, that is used as an instrument shutter. It blocks light from entering NIRSpec during calibration exposures and whenever NIRSpec is not being used, and serves as a mirror for internal lamp observations.
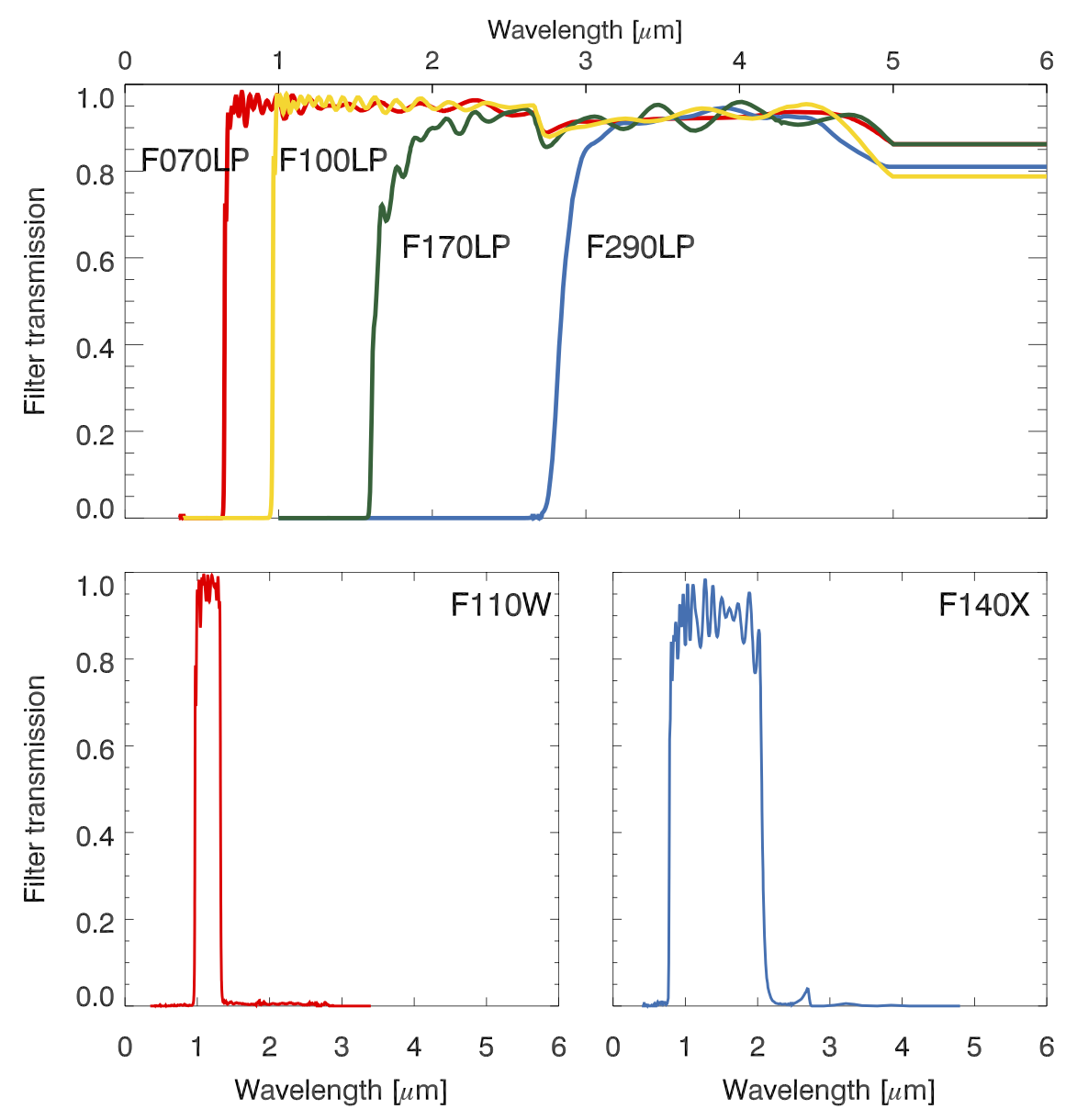
The transmission curves as a function of wavelength for the different filters for the NIRSpec instrument are shown in Figure 2. Files containing the tabulated data used to produce these curves can be downloaded from the following links. These are binary FITS tables that contain 2 columns: wavelength (μm) and throughout. These data are currently in use by the ETC (delivered October 2022).
jwst_nirspec_f070lp_trans.fits
jwst_nirspec_f100lp_trans.fits
jwst_nirspec_f170lp_trans.fits
jwst_nirspec_f290lp_trans.fits
Table 1. Transmission filters
| Name | Bandpass (µm) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| F140X | 0.8 to 2.0 | target acquisition |
| F110W | 1.0 to 1.3 | narrowband acquisition for brighter targets |
| F070LP | >0.7 | 0.7 to 1.3 µm spectra |
| F100LP | >1.0 | 1.0 to 1.9 µm spectra |
| F170LP | >1.7 | 1.7 to 3.2 µm spectra |
| F290LP | >2.9 | 2.9 to 5.3 µm spectra |
| CLEAR | 0.6 to 5.3 | target acquisition or for use with PRISM |
Note that the nominal spectral ranges for each filter may be shortened due to detector cutoffs. For the F070LP filter in particular there are blue end wavelength detector cutoffs that occur. The cutoff wavelengths depend on the target aperture location (slit or shutter). These cutoffs are described separately for each mode in the following articles: NIRSpec IFU Wavelength Ranges and Gaps, NIRSpec FS Wavelength Ranges and Gaps, NIRSpec BOTS Wavelength Ranges and Gaps, and NIRSpec MOS Wavelength Ranges and Gaps. The ETC can also be used to see where the cutoffs occur for all modes except MOS.
NIRSpec dispersers
NIRSpec has 7 dispersers in the GWA:
- three high resolution, R ~ 2,700, gratings (G140H, G235H, and G395H)
- three medium resolution, R ~ 1,000, gratings (G140M, G235M, and G395M)
- a low resolution, R ~ 100, double-pass prism (PRISM)
The full wavelength range of NIRSpec can be sampled in one exposure using the prism. However, each diffraction grating can only provide clean spectra over a factor of 2 in wavelength due to order contamination. The second order λ/2 spectra end up on exactly the same detector pixels as photons with wavelength λ (albeit with reduced efficiency). As a result, when using the diffraction gratings, the wavelength limit on the short side (blueward) is defined by the throughput of the long pass filters, and the limit on the long side (redward) is defined by the wavelength where second-order light contaminates the spectrum. To obtain data over the entire 0.6–5.3 µm wavelength range using the gratings, spectra over smaller wavelength ranges are obtained using matched dispersers and filters, and then combined.
To avoid order contamination, each disperser is only used with its paired transmission filter(s), as shown in Table 2. Also shown are each combined grating-filter wavelength range and the nominal resolving power, which is defined as the resolving power at the center of the nominal wavelength range. Grating transmissions for the NIRSpec medium and high resolution dispersers are presented in Figure 3, and the wavelength dependence of the resolving powers is shown in Figure 4.
The last position in the GWA is a plane mirror, which provides undispersed imaging of the sky and is only used for target acquisition or field position verification during science operations.
Grating wheel position sensor
The grating wheel position can vary slightly between exposures with different grating selections. There is a grating wheel position sensor that removes any zero point wavelength shift (in post processing) due to slight variations in the position of the grating wheel. NIRSpec is required to deliver a wavelength accuracy to better than 1/8 of a spectral resolution element, or approximately 15 km/s for spectra taken with the high-resolution gratings. The instrument model wavelength calibration is expected to meet the wavelength calibration accuracy requirement, making autocals unnecessary. Autocals can add significant overhead to an observation.
Table 2. Available disperser-filter combinations
| Disperser-filter combination | Nominal resolving power | Wavelength range † (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| G140M/F070LP | ~1,000 | 0.70–1.27 |
| G140M/F100LP | 0.97–1.84 | |
| G235M/F170LP | 1.66–3.07 | |
| G395M/F290LP | 2.87–5.10 | |
| G140H/F070LP | ~2,700 | 0.81–1.27 |
| G140H/F100LP | 0.97–1.82 | |
| G235H/F170LP | 1.66–3.05 | |
| G395H/F290LP | 2.87–5.14 | |
| PRISM/CLEAR | ~100 | 0.60-5.30 |
† Wavelength range values presented here are approximate. Note that the nominal spectral ranges for medium and high-resolution dispersers may be shortened due to red-end detector cutoffs. The cutoff wavelengths depend on the target aperture location (slit or shutter). Detailed limits on the wavelength ranges and gaps are found in the ETC.
Dispersion curves for the NIRSpec dispersers
The dispersion and resolution curves as a function of wavelength for the different dispersers for the NIRSpec instrument are shown in Figures 5–11. Files containing the tabulated data used to produce these curves can be downloaded from the following links. These are binary fits tables that contain 3 columns: wavelength (μm), dispersion (μm/pixel) and resolution (λ⁄Δλ, unitless). These data are currently in use by the ETC (delivered June 2016).