NIRCam Optics
The JWST NIRCam optical elements include dichroics, filters, weak lenses, grisms, as well as coronagraph occulting masks and Lyot stops.
On this page
NIRCam's 2 modules (A and B) receive light relatively close to on-axis from the JWST Optical Telescope Element (OTE), as shown in the field of view in Figure 1.
Figure 1. NIRCam modules footprint in the JWST field of view
Optical path
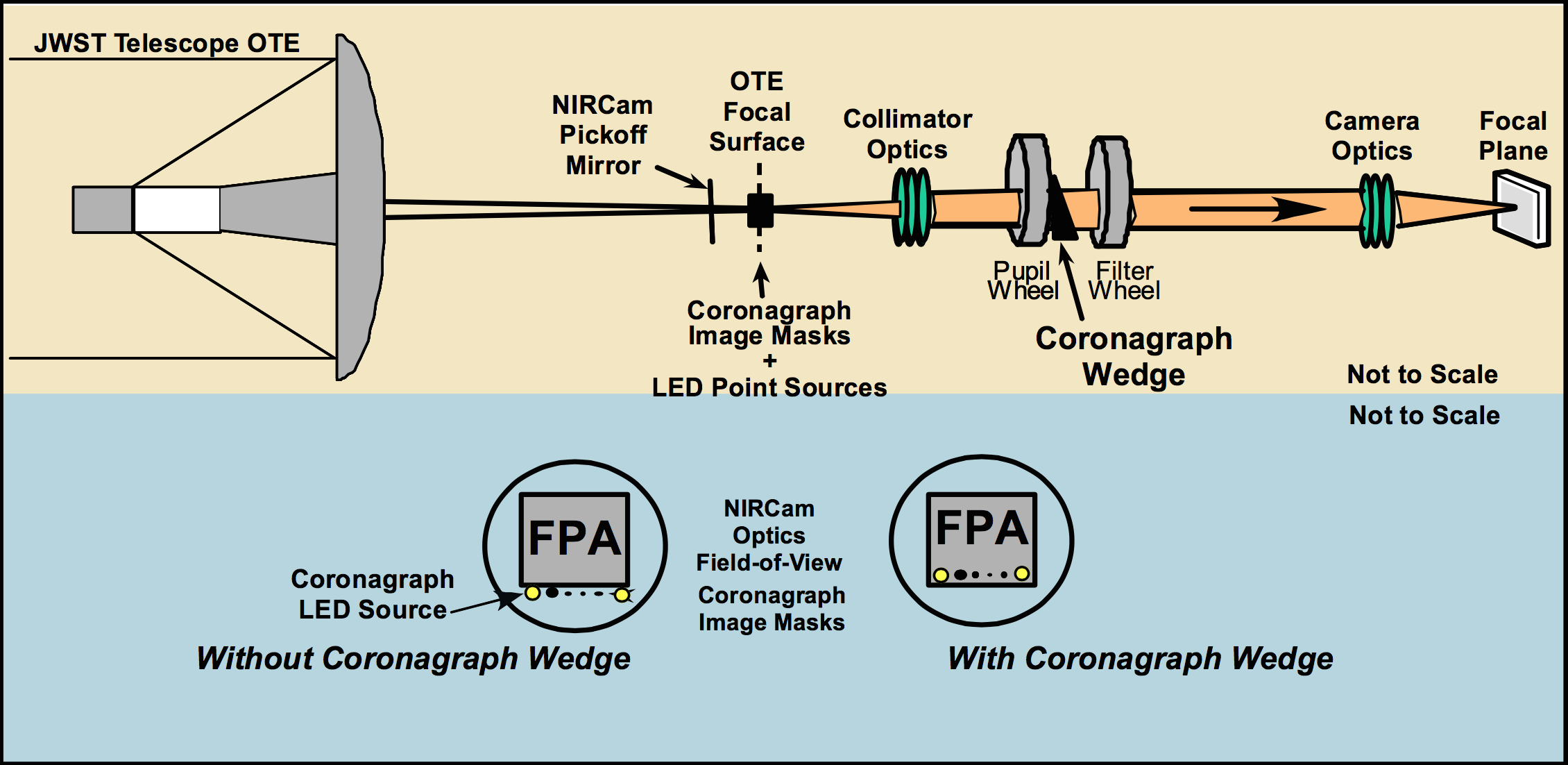
From the NIRCam pickoff mirror, within each module, light passes through these components in the following order:
- (Optionally) The coronagraph occulting masks, located at the OTE focal surface
- Collimator optics
- Dichroic, reflecting short wavelength light (0.6–2.3 µm) and transmitting long wavelength light (2.4–5.0 µm)
- Pupil wheel (including coronagraph Lyot stops each with an optical wedge; weak lenses for short wavelengths; grisms for long wavelengths)
- Filter wheel (including filters and a short wavelength weak lens)
- Camera optics
- (Optionally in short wavelength channel) Pupil imaging lens (PIL) for wavefront sensing and alignment measurements
- Detectors (in the focal plane)
Figure 2. NIRCam optical train
Lower half of figure: The detector view, at the focal plane assembly (FPA), of incoming light with and without a coronagraph wedge in the optical path. The coronagraph wedges are included on Lyot stop elements on each pupil wheel. © Somerstein & Truong 2005.
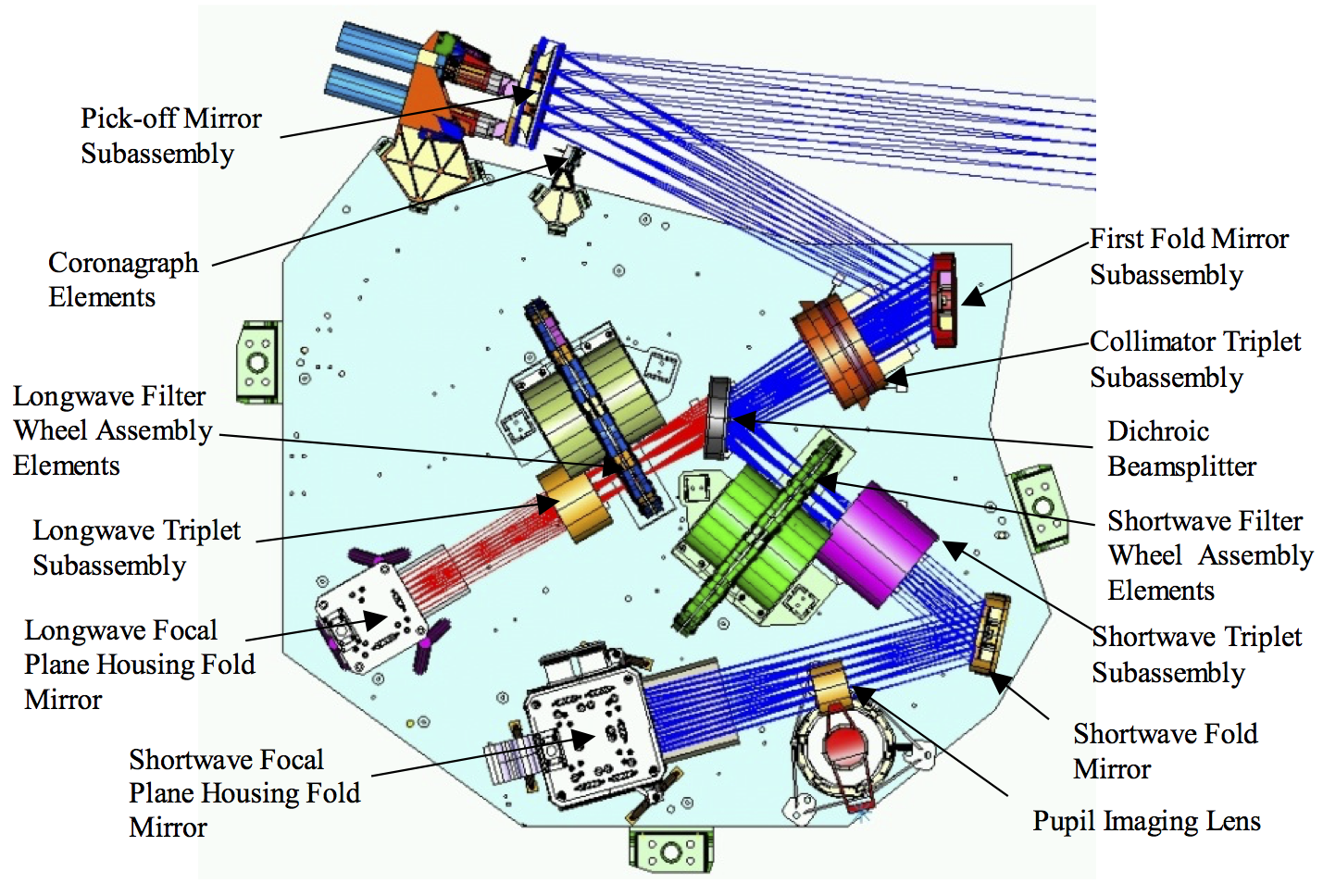
Figure 3. NIRCam optical train in one module
References
Greenhouse, M. et al. 2011, SPIE 814606G
Status of the James Webb Space Telescope integrated science instrument module system
Somerstein, S. F., Truong, G.D. 2005, SPIE 590407
NIRCam optical calibration sources
Huff, L. 2005, SPIE 590404
NIRCam instrument optics