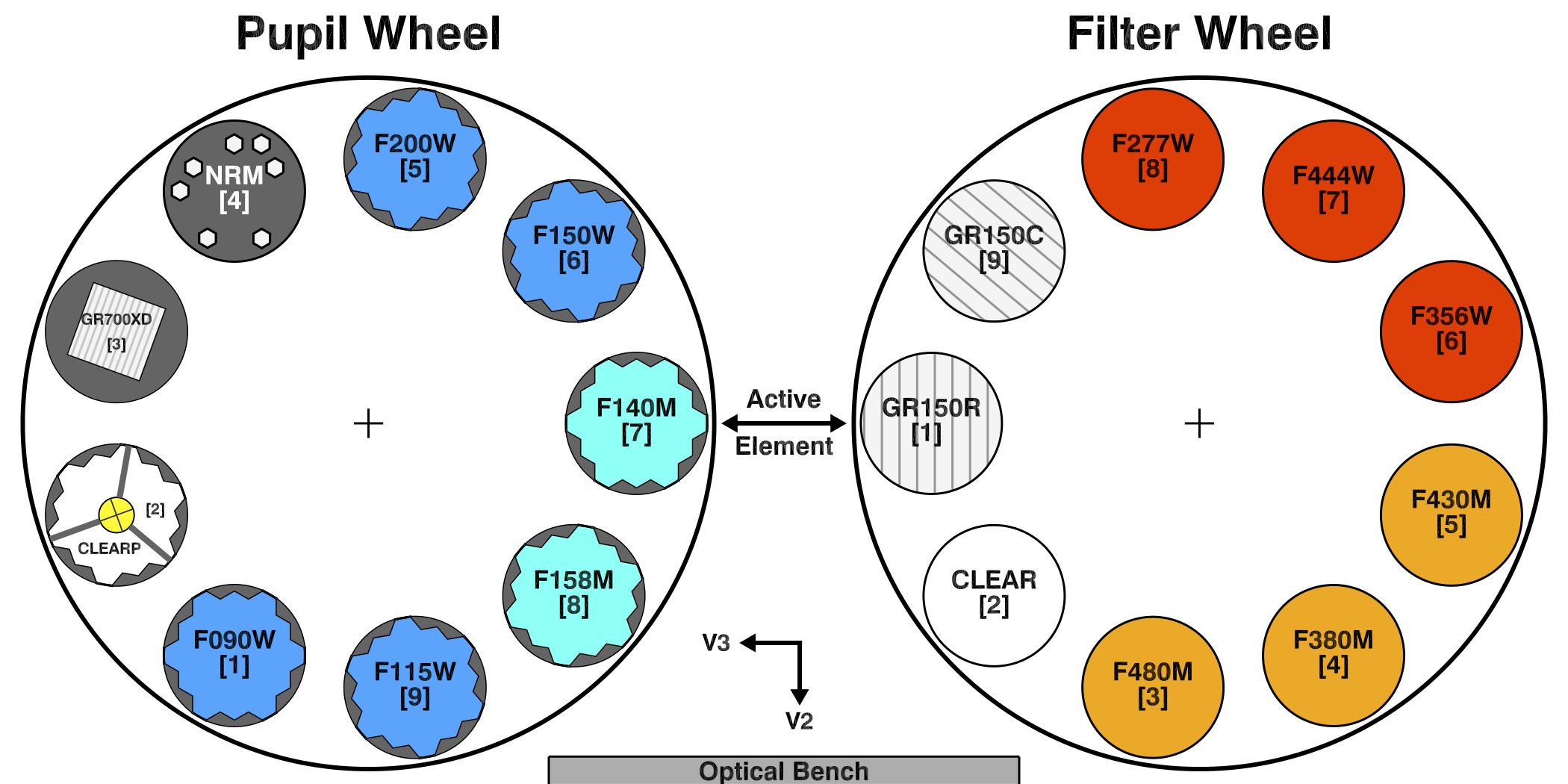
NIRISS Pupil and Filter Wheels
The pupil wheel and filter wheel house the filters, low- and high-resolution grisms, and aperture mask that enable the 4 observing modes of JWST NIRISS.
On this page
See also: NIRISS Instrumentation, NIRISS Filters, NIRISS GR700XD Grism, NIRISS GR150 Grisms, NIRISS Non-Redundant Mask
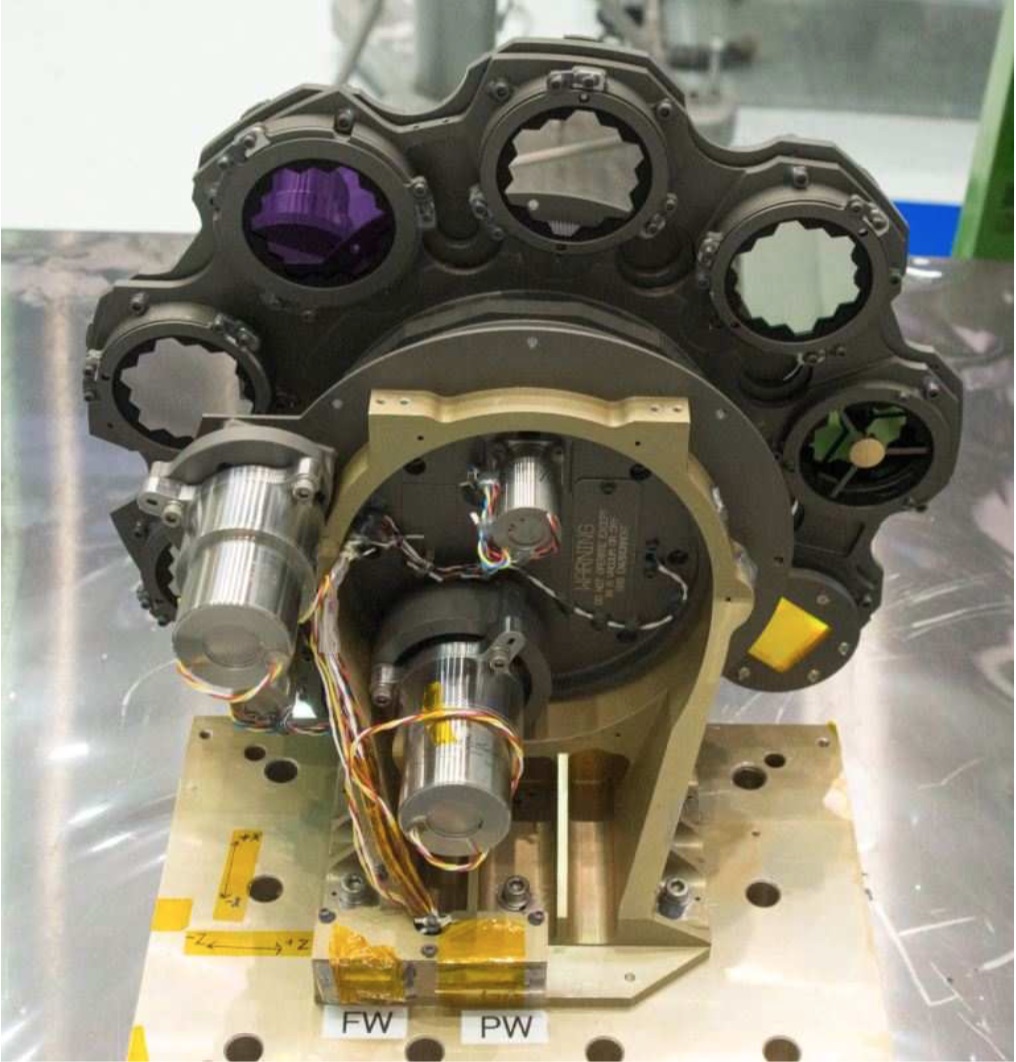
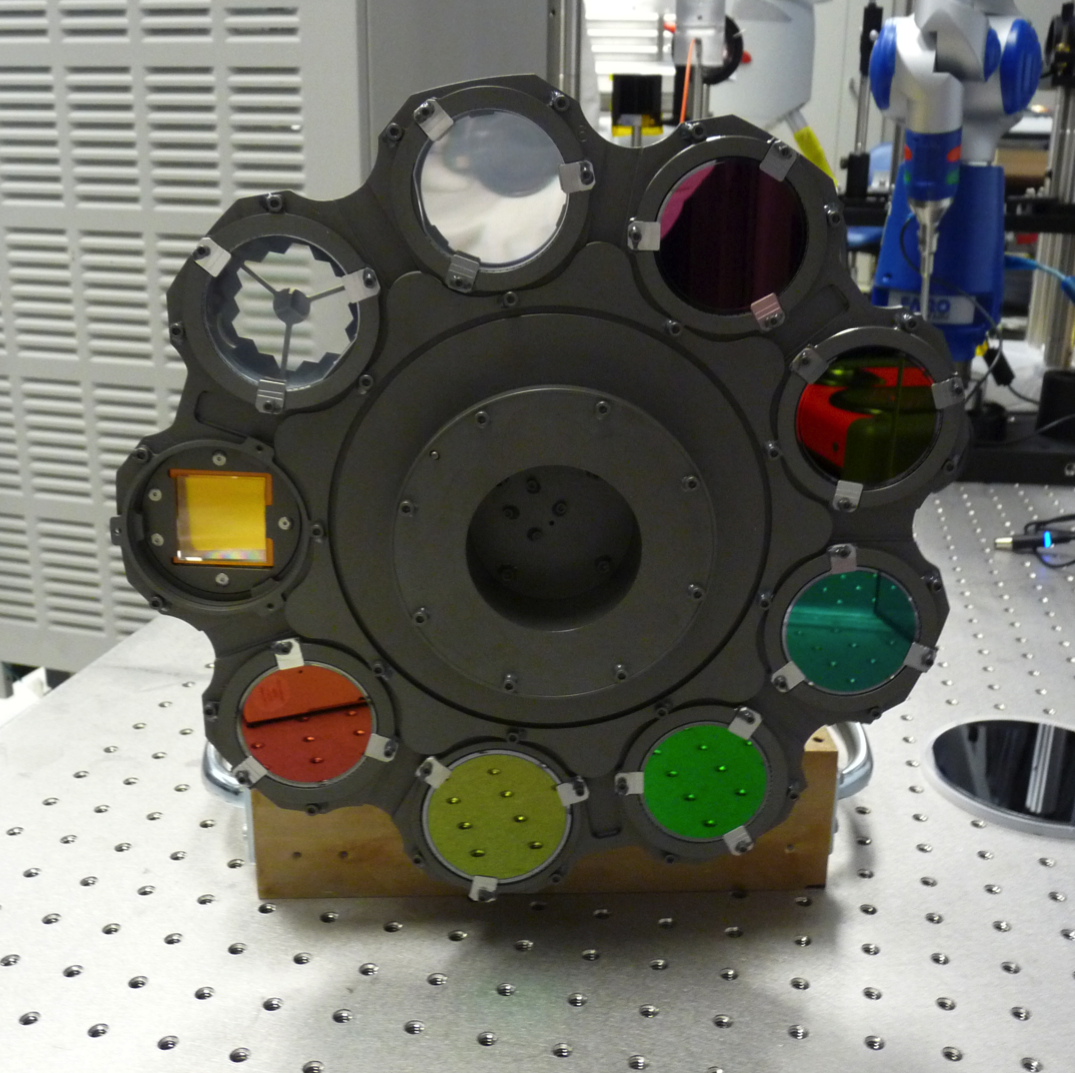
NIRISS has a dual-wheel assembly that consists of the pupil wheel (PW) and filter wheel (FW) that are placed back-to-back as shown in Figure 1. Each wheel has 9 positions. Light from the collimator first passes through the "active" element in the pupil wheel and then through the "active" element of the filter wheel. The 2 wheels can be rotated independently to select the specific combinations of optical elements that define the NIRISS observing modes.
Contents of the pupil wheel
See also: NIRISS Filters, NIRISS GR700XD Grism, NIRISS Non-Redundant Mask, NIRISS Wide Field Slitless Spectroscopy, NIRISS Single Object Slitless Spectroscopy, NIRISS Aperture Masking Interferometry, NIRISS Imaging
Table 1. Contents of the pupil wheel
| Position | Element name | Description | Observing mode | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F090W | Broadband filter centered at 0.90 μm | WFSS, Imaging | |
| 2 | CLEARP | Empty slot | Imaging | Includes the permanently mounted pupil alignment reference (PAR), which was used for optical alignment during assembly and ground-based testing. It reduces transmission through the slot by ~16%. |
| 3 | GR700XD | Grism with resolving power ~700 at 1.4 μm. | SOSS | Includes a cylindrical lens to broaden spectral orders in the spatial direction |
| 4 | NRM | Aperture mask | AMI | Net transmission of ~15% |
| 5 | F200W | Broadband filter centered at 2.00 μm | WFSS, Imaging | |
| 6 | F150W | Broadband filter centered at 1.50 μm | WFSS, Imaging | |
| 7 | F140M | Medium-band filter centered at 1.40 μm | WFSS, Imaging | |
| 8 | F158M | Medium-band filter centered at 1.58 μm | WFSS, Imaging | |
| 9 | F115W | Broadband filter centered at 1.15 μm | WFSS, Imaging |
Contents of the filter wheel
See also: NIRISS Filters, NIRISS GR150 Grisms, NIRISS Wide Field Slitless Spectroscopy, NIRISS Single Object Slitless Spectroscopy, NIRISS Aperture Masking Interferometry, NIRISS Imaging
Table 2. Contents of the filter wheel
| Position | Element name | Description | Observing mode | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GR150R | Grism with resolving power ~150 at 1.4 μm | WFSS | Disperses along the direction of "fast" detector readout. |
| 2 | GR150C | Grism with resolving power ~150 at 1.4 μm | WFSS | Disperses along the direction of "slow" detector readout. |
| 3 | F277W | Broadband filter centered at 2.77 μm | AMI, Imaging | |
| 4 | F444W | Broadband filter centered at 4.44 μm | Imaging | |
| 5 | F356W | Broadband filter centered at 3.56 μm | Imaging | |
| 6 | F430M | Medium-band filter centered at 4.30 μm | AMI, Imaging | |
| 7 | F380M | Medium-band filter centered at 3.80 μm | AMI, Imaging | |
| 8 | F480M | Medium-band filter centered at 4.80 μm | AMI, Imaging | |
| 9 | CLEAR | Empty slot | SOSS, Imaging |
Operation and overheads
See also: JWST Observing Overheads and Time Accounting Overview
The pupil and filter wheels can rotate in either direction. Consequently, any optical element can be placed into the "active" position by a move of 4 positions or fewer. The wheel mechanisms have angular repeatability of ±0.1651° for the pupil wheel and ±0.1585° for the filter wheel. The exact angular position of each wheel is recorded in a FITS header keyword (PWCPOS, FWCPOS), which may be used to refine knowledge of the location or tilt of spectral traces on the detector, for example.
References
Martel, A. 2016 JWST-STScI-004964
Analysis of NIRISS CV3 Data: The Repeatability of the Pupil Wheel and the Filter Wheel