NIRISS Wide Field Slitless Spectroscopy
The wide field slitless spectroscopy (WFSS) mode of JWST’s Near Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (NIRISS) enables low-resolution (R ≈ 150) spectroscopy between 0.8–2.2 μm, over the 2.2’ × 2.2’ FOV.
On this page
See also: NIRISS Wide Field Slitless Spectroscopy APT Template, NIRISS WFSS Recommended Strategies, NIRISS WFSS Science Use Case
The wide field slitless spectroscopy (WFSS) mode of NIRISS enables low-resolution (R ≈ 150) spectroscopy over the wavelength range 0.8–2.2 μm for all objects within the 2.2’ × 2.2’ field of view (FOV) of the NIRISS detector (Willott et al. 2022).
The NIRISS WFSS mode is particularly useful for detecting high-redshift emission-line galaxies and can be used very efficiently as a parallel observing mode with other instruments.
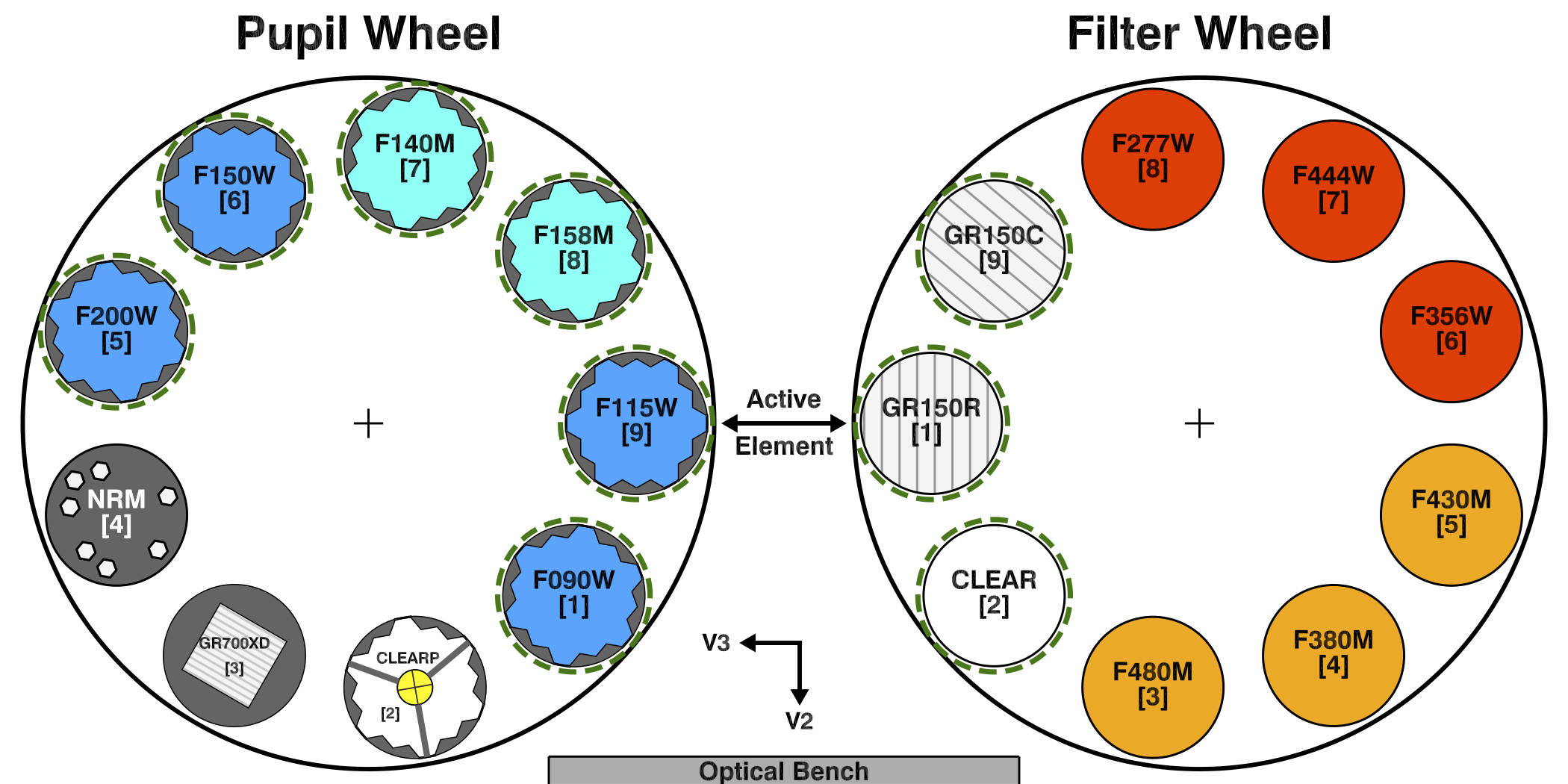
The WFSS mode uses a pair of identical grisms (GR150R and GR150C) that are mounted in the filter wheel so that their respective dispersion directions are perpendicular to each other on the detector.
- The GR150R grism disperses along the direction of fast readout.
- The GR150C grism disperses along the direction of slow readout.
Data acquired with both dispersion directions helps to disentangle blended spectra in crowded fields. The NIRISS WFSS Recommended Strategies article discusses using both grisms in more detail.
WFSS observations are obtained by using one or both of the grisms in combination with a wide- or medium-band blocking filter located in the pupil wheel (PW). The blocking filters limit the wavelength coverage and therefore the extent of spectra on the detector, which reduces the blending of spectral traces from objects distributed throughout the FOV.
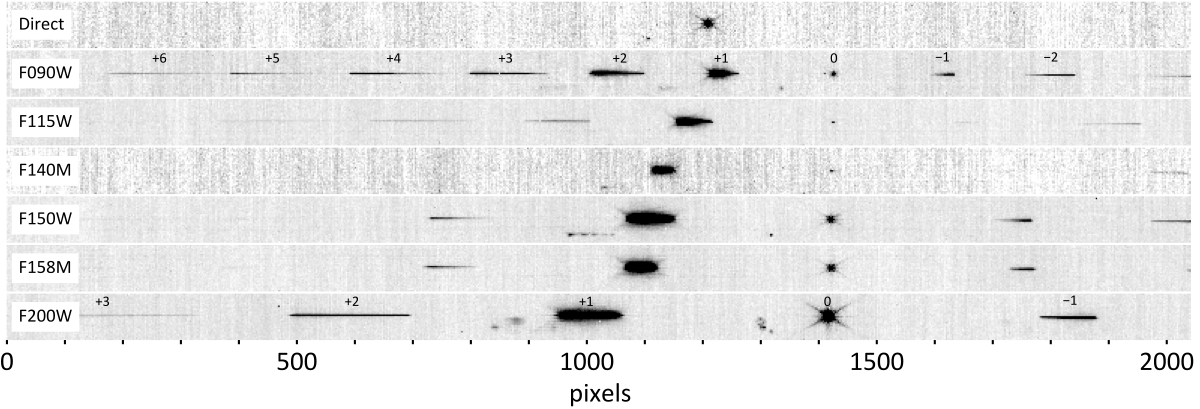
Layout of spectral orders
WFSS observation sequence
See also: NIRISS WFSS Template APT Guide, NIRISS GR150 Grisms, NIRISS Filters, NIRISS WFSS Dithers, NIRISS Mosaics
An observation in the WFSS mode proceeds as follows:
- A blocking filter is selected in the PW; the FW is set to CLEAR.
- A single (i.e., non-dithered) image of the scene is taken, called the the "pre-image."
- One of the GR150 grisms is selected, either GR150C or GR150R.
- Dithered grism images are taken.
- At the last dither position, the CLEAR element is selected again and a single image of the scene is taken, called the "post-image." As of APT 2020.2, this "post-image" can optionally be executed with 2 extra dithers, if desired.
- Optional: select a different blocking filter and repeat steps 1–5 with the same grism.
- Optional: select the other GR150 grism and repeat steps 1–6.
Exercising optional step 6 will increase the wavelength coverage for spectra of the objects in the scene, while exercising step 7 will produce observations of the scene with spectra dispersed in orthogonal directions on the detector.
The pre- and post-image through the relevant blocking filter is required:
- to enable proper identification of object(s) seen in the grism image(s), and
- to determine the origin of the absolute wavelength scale for the grism spectra for each object in the field.
Words in bold are GUI menus/
panels or data software packages;
bold italics are buttons in GUI
tools or package parameters.
WFSS blocking filters
See also: NIRISS Filters
The NIRISS WFSS mode uses 6 blocking filters in the PW. These are the 4 wideband filters (F090W, F115W, F150W, and F200W), and 2 medium-band filters (F140M, and F158M). Figures 3 and 4 provide different visualizations of the wavelength coverage and spatial extent of the traces isolated by the blocking filters.
WFSS subarrays
See also: NIRISS Detector Subarrays
Subarrays are not available for general observations in the WFSS mode. However, to support calibration observations of brighter standard stars, subarrays are available in the external calibration template for use by STScI instrument scientists. More details are provided in the NIRISS subarrays article.
WFSS dither patterns
See also: NIRISS WFSS Dithers, NIRISS Dithers
The NIRISS PSF is undersampled in the wavelength range (0.8–2.2 μm) covered by the WFSS mode. For compact sources, a significant fraction of the flux in WFSS spectra is concentrated in the central few pixels of the cross-dispersion profile. Dithering is therefore required for WFSS observations in order to mitigate the impact of hot pixels, cosmic rays, and residual flat field errors, and also to improve the effective spatial resolution.
Since WFSS observing programs are likely to use both the GR150R and GR150C grisms in an observing sequence, optimized dither patterns have been defined for this mode. Details on the available dither patterns are provided on the NIRISS WFSS dithers page.
Simulating WFSS observations
See also: MIRAGE JWST Data Simulator
The software for simulating NIRISS WFSS data and the necessary grism configuration files can be obtained from the MIRAGE (Multi-Instrument RAmp GEnerator) github repository.
There may be cases where a particular source of interest is targeted within a WFSS field and a user may want to minimize contamination of this spectrum from overlapping spectra of nearby sources. Specific position angles may mitigate such contamination. The NIRISS grism overlap tool can be used to examine a NIRISS WFSS scene at different orientations to identify which orient ranges may be less affected by spectral overlap.
References
Dixon, V., Willott, C., 2013, STScI Newsletter, Volume 30, issue 2
Wide-Field Slitless Spectroscopy with Webb's NIRISS
Willott, C. J., Doyon, R., Albert, L., et al. 2022, PASP, 134, 1032
The Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph for the James Webb Space Telescope. II. Wide Field Slitless Spectroscopy